Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Advancing Korean nationwide registry for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic sampling approach utilizing the Korea Central Cancer Registry database
- Bo Hyun Kim, E Hwa Yun, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Geun Hong, Jun Yong Park, Ju Hyun Shim, Eunyang Kim, Hyun-Joo Kong, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Suk Lim
- J Liver Cancer. 2024;24(1):57-61. Published online March 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2024.03.03
- 348 Views
- 20 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
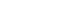
Supplementary Material - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presents a substantial public health challenge in South Korea as evidenced by 10,565 new cases annually (incidence rate of 30 per 100,000 individuals), in 2020. Cancer registries play a crucial role in gathering data on incidence, disease attributes, etiology, treatment modalities, outcomes, and informing health policies. The effectiveness of a registry depends on the completeness and accuracy of data. Established in 1999 by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Korea Central Cancer Registry (KCCR) is a comprehensive, legally mandated, nationwide registry that captures nearly all incidence and survival data for major cancers, including HCC, in Korea. However, detailed information on cancer staging, specific characteristics, and treatments is lacking. To address this gap, the KCCR, in partnership with the Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA), has implemented a systematic approach to collect detailed data on HCC since 2010. This involved random sampling of 10-15% of all new HCC cases diagnosed since 2003. The registry process encompassed four stages: random case selection, meticulous data extraction by trained personnel, expert validation, anonymization of personal data, and data dissemination for research purposes. This random sampling strategy mitigates the biases associated with voluntary reporting and aligns with stringent privacy regulations. This innovative approach positions the KCCR and KLCA as foundations for advancing cancer control and shaping health policies in South Korea.

Original Article
- Clinical characteristics and prognosis of Korean patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with respect to etiology
- Wonjoon Jang, Hye Won Lee, Jae Seung Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2022;22(2):158-166. Published online September 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.2022.09.18

- 2,762 Views
- 66 Downloads
- 7 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
The profile of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has changed globally; the role of etiology in predicting prognosis of HCC patients remains unclear. We aimed to analyze the characteristics and prognosis of Korean patients with HCC according to disease etiology.
Methods
This retrospective observational study included patients diagnosed with HCC between 2010 and 2014 in a single center in Korea. Patients with HCC aged <19 years old, had coinfection with other viral hepatitis, had missing follow-up data, were Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage D, or died before 1 month were excluded.
Results
A total of 1,595 patients with HCC were analyzed; they were classified into the hepatitis B virus (HBV) group (1,183 [74.2%]), hepatitis C virus (HCV) group (146 [9.2%]), and non-B non-C (NBNC) group (266 [16.7%]). The median overall survival of all patients was 74 months. The survival rates at 1, 3, and 5 years were 78.8%, 62.0% and 54.9% in the HBV group; 86.0%, 64.0%, and 48.6% in the HCV group; and 78.4%, 56.5%, and 45.9% in the NBNC group, respectively. NBNC-HCC has a poorer prognosis than other causes of HCC. Survival was significantly longer in the HBV group with early-stage HCC than in the NBNC group. Furthermore, survival was shorter in patients with early-stage HCC and diabetes mellitus (DM) than in those without DM.
Conclusions
The etiology of HCC affected clinical characteristics and prognosis to some extent. NBNC-HCC patients showed shorter overall survival than viral-related HCC patients. Additionally, the presence of DM is an additional important prognostic factor in patients with early-stage HCC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis
Log Young Kim, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Young Chang, Hoongil Jo, Young Youn Cho, Sangheun Lee, Dong Hyeon Lee, Jae Young Jang
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Surgical Resection and Radiofrequency Ablation in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Jun Il Kim, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park, Jeong-Ju Yoo
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(3): 1055. CrossRef - Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Followed by Acute Hepatitis A Infection: Case Report
Min-Woo An, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jin Kuk Kim, Ahrim Moon, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 819. CrossRef - Validation of MELD 3.0 scoring system in East Asian patients with cirrhosis awaiting liver transplantation
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jong-In Chang, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Liver Transplantation.2023; 29(10): 1029. CrossRef - A nationwide study on the current treatment status and natural prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Jayoun Lee, Gi Hong Choi, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ah Park
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Statin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis B: an emulated target trial using longitudinal nationwide population cohort data
Dong Hyun Sinn, Danbee Kang, Yewan Park, Hyunsoo Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Juhee Cho, Geum-Youn Gwak
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Addition of Kidney Dysfunction Type to MELD-Na for the Prediction of Survival in Cirrhotic Patients Awaiting Liver Transplantation in Comparison with MELD 3.0 with Albumin
Kyeong-Min Yeom, Jong-In Chang, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Ji Eun Moon, Dong Hyun Sinn, Young Seok Kim, Sang Gyune Kim
Diagnostics.2023; 14(1): 39. CrossRef
- The Epidemiology of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Korea: 15-Year Analysis

Case Report
- A Case of Lymphocyte-Rich Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Patient Who Was Treated for Colon Cancer
- Jae Won Song, Ho Soo Chun, Jae Seung Lee, Hye Won Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Young Nyun Park, Dai Hoon Han, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2021;21(1):69-75. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.21.1.69
- 3,541 Views
- 84 Downloads
- 2 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
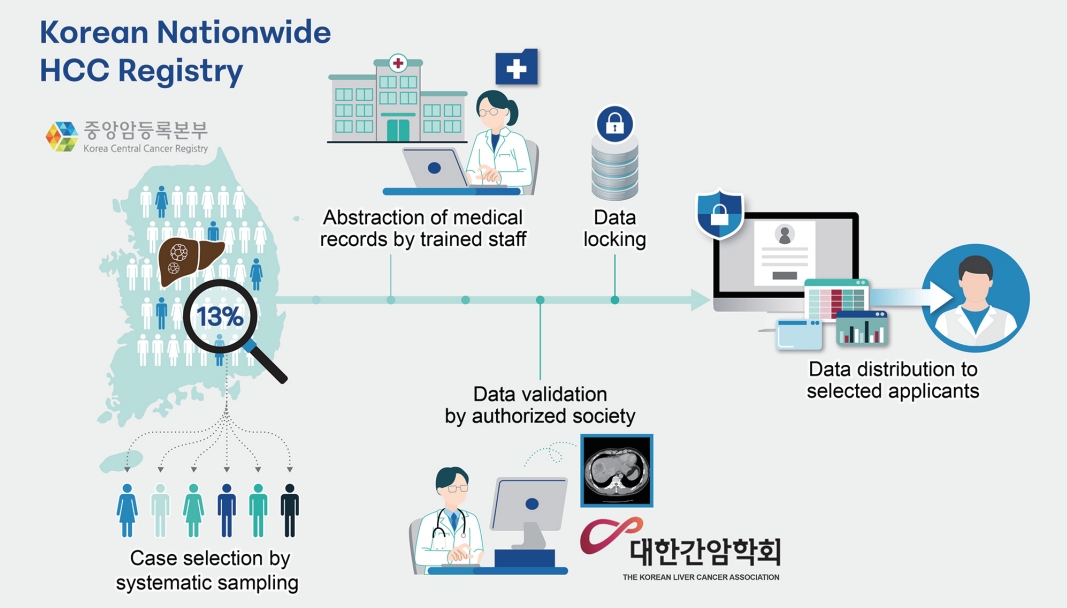
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) primarily originates in the liver with hepatic differentiation. However, HCCs are not homogenous, and approximately 35% of HCC cases are classified as histopathological variants that present distinct pathologic characteristics. In particular, the lymphocyte-rich variant is the rarest subtype accounting for less than 1% of HCCs, which is not well known to date about molecular features and pathophysiology. Herein, we present a case of a patient who was suspected of metastatic liver cancer and confirmed as lymphocyte-rich HCC pathologically. A 78-year-old woman who underwent a right hemicolectomy for colon cancer was referred to our hospital for a newly detected liver mass. We could not make a decision because of insufficient evidence for diagnosis from imaging studies. After resection, we found that it was a lymphocyte-rich HCC. The pathologic features and prognostic trends of this subtype are also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterization of lymphocyte‐rich hepatocellular carcinoma and the prognostic role of tertiary lymphoid structures
Bokyung Ahn, Hee‐Sung Ahn, Jinho Shin, Eunsung Jun, Eun‐Young Koh, Yeon‐Mi Ryu, Sang‐Yeob Kim, Chang Ohk Sung, Ju Hyun Shim, JeongYeon Hong, Kyunggon Kim, Hyo Jeong Kang
Liver International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Uncommon variants of hepatocellular carcinoma: Not one size fits all
Reetu Kundu, Nalini Gupta, Debajyoti Chatterjee, Ajay Duseja
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2022; 50(1): 28. CrossRef
- Characterization of lymphocyte‐rich hepatocellular carcinoma and the prognostic role of tertiary lymphoid structures

Original Article
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(2):135-147. Published online September 30, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.2.135
- 4,534 Views
- 158 Downloads
- 15 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Considering the high prevalence and mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in Korea, accurate statistics for HCC are important. We evaluated the characteristics of Korean patients with newly diagnosed HCC.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated data from the Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR). The baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of 4,572 patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2012 and 2014 were investigated.
Results
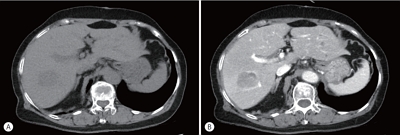
At the time of HCC diagnosis, the median age was 60.0 years, with male predominance (79.6%). Hepatitis B virus infection was the most common etiology (59.1%). The rates of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stages 0, A, B, C, and D at diagnosis were 3.9%, 36.9%, 12.5%, 39.4%, and 7.3%, respectively. The proportion of very early or early stage HCC at diagnosis (BCLC stage 0 or A) in the 2012-2014 cohort was significantly lower than that in the 2008-2011 cohort (40.8% vs. 48.3%, P<0.001). Transarterial therapy (37.5%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by surgical resection (19.8%), best supportive care (19.1%), and local ablation (10.6%). The median OS was 2.9 years, and the 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 67.7%, 49.3% and 41.9%, respectively. The OS rate of the 2012-2014 cohort was significantly higher than that of the 2008-2011 cohort (log-rank, P<0.001).
Conclusions
The OS of HCC patients registered in the KPLCR between 2012 and 2014 significantly improved. Nevertheless, as about half of the HCC patients were diagnosed at an advanced stage, vigorous and optimized HCC screening strategies should be implemented. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors associated with the survival outcomes of patients with untreated hepatocellular carcinoma: An analysis of nationwide data
Min Jung Kwon, Soy Chang, Ji Hoon Kim, Ji Won Han, Jeong Won Jang, Jong Young Choi, Seung Kew Yoon, Pil Soo Sung
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical practice guideline and real-life practice in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Korean perspective
Myung Ji Goh, Dong Hyun Sinn, Jong Man Kim, Min Woo Lee, Dong Ho Hyun, Jeong Il Yu, Jung Yong Hong, Moon Seok Choi
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(2): 197. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Nomogram for predicting overall survival in patients with large (>5 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma based on real-world practice
Nalee Kim, Jeong Il Yu, Hee Chul Park, Jung Yong Hong, Ho Yeong Lim, Myung Ji Goh, Yong-Han Paik
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 350. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - A case report of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy and sorafenib combination therapy followed by metastasectomy of lung and muscle metastases
Sang Yi Moon, Sang Young Han, Yang-Hyun Baek
Journal of Liver Cancer.2022; 22(1): 57. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 583. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Korean Journal of Radiology.2022; 23(12): 1126. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Adjuvant Immunotherapy With Cytokine-Induced Killer Cell for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on a Randomized Controlled Trial and Real-World Data
Jeong-Yeon Cho, Sun-Hong Kwon, Eui-Kyung Lee, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Hye-Lin Kim
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy and Radiofrequency Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Refractory to Transarterial Chemoembolization and Vascular Variation: A Case Study
Sang Yi Moon, Sang Young Han, Yang-Hyun Baek
Kosin Medical Journal.2021; 36(2): 161. CrossRef
- Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly

Case Report
- Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
- Jaewoong Kim, Jin Won Chang, Jun Yong Park
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):72-77. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.72

- 4,573 Views
- 137 Downloads
- 1 Citation
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Over the past decade, standard first-line systemic treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has been based on sorafenib, a multi-kinase inhibitor. Regorafenib, another tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is the only second-line therapy that has been globally approved after progression under sorafenib treatment. Recently, immunotherapeutic agents have emerged as promising treatment options in many different malignancies, including advanced HCC. Nivolumab is the first immunotherapy approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in HCC patients with advanced-stage second-line after sorafenib failure. In this report, a case of advanced HCC with multiple lung metastases in which a complete response and maintained progression-free status was achieved with nivolumab, following the failure of transarterial chemoembolization and sorafenib is presented. We hope this report may help expand the clinical application of second-line treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report
Ji Eun Han, Hyo Jung Cho, Soon Sun Kim, Jae Youn Cheong
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(2): 169. CrossRef
- Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with multiple lung metastasis completely cured using nivolumab: a case report

Original Articles
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea Between 2008 and 2011: an Analysis of Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
- Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Young Eun Chon, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Young-Joo Won, Eunyang Kim, Jeong-Hoon Lee
- J Liver Cancer. 2020;20(1):41-52. Published online March 31, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.41

- 5,033 Views
- 193 Downloads
- 15 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Backgrounds/Aims
Backgrounds/Aims: In Korea, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and results in the second-highest cancer death rate among all cancers. We aimed to describe the characteristics of patients who were newly diagnosed with HCC in Korea between 2008 and 2011.
Methods
The Korean Primary Liver Cancer Registry (KPLCR) is a random sample consisting of approximately 15% of patients with newly diagnosed primary liver cancer registered in the Korean Central Cancer Registry. We investigated the baseline characteristics, treatment modalities, and overall survival (OS) of patients with HCC registered in the KPLCR between 2008 and 2011.
Results
A total of 6,083 patients were histologically or radiologically diagnosed with HCC. The hepatitis B virus was the predominant HCC etiology (72.0%). According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, stages 0, A, B, C, and D accounted for 8.6%, 39.7%, 11.5%, 33.8%, and 6.9%, respectively. Transarterial therapy (41.7%) was the most commonly performed initial treatment, followed by best supportive care (21.7%), surgical resection (16.7%), and local ablation therapies (10.6%). The overall rate of adherence to the BCLC treatment guideline was only 37.7%. The 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates were 65.6%, 46.2%, and 36.8%, respectively.
Conclusions
Between 2008 and 2011, approximately half of patients with HCC (48.3%) were candidates for curative treatment (BCLC stage 0 or A), but one-third of patients (33.8%) had advanced HCC (BCLC stage C). Transarterial therapy was the most commonly conducted initial treatment and the 5-year OS rate was 36.8% in this period. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma
Josep M. Llovet, Roser Pinyol, Mark Yarchoan, Amit G. Singal, Thomas U. Marron, Myron Schwartz, Eli Pikarsky, Masatoshi Kudo, Richard S. Finn
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology.2024; 21(4): 294. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence is decreasing in Korea but increasing in the very elderly
Young Eun Chon, Seong Yong Park, Han Pyo Hong, Donghee Son, Jonghyun Lee, Eileen Yoon, Soon Sun Kim, Sang Bong Ahn, Soung Won Jeong, Dae Won Jun
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(1): 120. CrossRef - Implications of the first edition of the Korean expert consensus-based practice recommendations for transarterial chemoembolization in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Jin Wook Chung
Journal of Liver Cancer.2023; 23(2): 235. CrossRef - Surgical resection versus ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma: The debate is still open
Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 174. CrossRef - Cause of death and cause-specific mortality for primary liver cancer in South Korea: A nationwide population-based study in hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Bo Hyun Kim, Dahhay Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Young-Joo Won, Hyunsoon Cho
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(2): 242. CrossRef - Impact of expanding hepatitis B treatment guidelines: A modelling and economic impact analysis
Young‐Suk Lim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Jae‐Jun Shim, Homie Razavi, Devin Razavi‐Shearer, Dong Hyun Sinn
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2022; 56(3): 519. CrossRef - Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: It is time to move forward
Bo Hyun Kim, Yuri Cho, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2022; 28(4): 810. CrossRef - Therapeutic Decision Making in Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Age and Child–Pugh Class: A Nationwide Cohort Analysis in South Korea
Sunmin Park, Chai Hong Rim, Young Kul Jung, Won Sup Yoon, Alessandro Granito
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Outcome of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor and Molecular Target Agent Combination for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Beyond Sorafenib Era
Nae-Yun Heo
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 77(3): 145. CrossRef - Rare Case of Pyogenic Brain Abscess after Transarterial Chemoembolization in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
Jun-Ho Myeong, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Sang Gyune Kim, Young Seok Kim
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 81. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea: an Analysis of the 2015 Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Jun Sik Yoon, Han Ah Lee, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Hyun Sinn, Dong Ho Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Ju-Yeon Cho, Jonggi Choi, Young Chang, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2021; 21(1): 58. CrossRef - Glucose Variability and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Eun Ju Cho, Kyungdo Han, Soo Seong Heo, Bo-Yeon Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Su Jong Yu
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2021; 30(5): 974. CrossRef -
Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive fraction of alpha-fetoprotein improves diagnostic accuracy for hepatocellular carcinoma
Han Ah Lee, Yoo Ra Lee, Young-Sun Lee, Young Kul Jung, Ji Hoon Kim, Hyunggin An, Hyung Joon Yim, Yoon Tae Jeen, Jong Eun Yeon, Kwan Soo Byun, Yeon Seok Seo
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(28): 4687. CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef - Efficacy of Local Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involving the Inferior Vena Cava and/or Right Atrium
Han Ah Lee, Chai Hong Rim
Journal of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2020; Volume 7: 435. CrossRef
- Adjuvant and neoadjuvant immunotherapies in hepatocellular carcinoma

- Serum PD-1 Levels Change with Immunotherapy Response but Do Not Predict Prognosis in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hye Won Lee, Kyung Joo Cho, Soon Young Shin, Ha Yan Kim, Eun Ju Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han
- J Liver Cancer. 2019;19(2):108-116. Published online September 30, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.19.2.108

- 5,373 Views
- 151 Downloads
- 5 Citations
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material - Background/Aim
s: Programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) is a promising new target for treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A high expression level of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a possible prognostic indicator for poor outcome in other malignancies. Here, we investigated the clinical significance of PD-1 and PD-L1 in patients with HCC.
Methods
We enrolled patients with HCC who underwent surgical resection at Severance Hospital between 2012 and 2017 and investigated the levels of PD-L1 in HCC tissues (tPD-L1) and PD-L1/PD-1 in serum (sPD-L1/sPD-1). We also aimed to determine whether expression levels correlated with clinical and histological features.
Results
A total of 72 patient samples were analyzed. The median sPD-L1 and sPD-1 levels were 25.72 and 341.44 pg/mL, respectively. A positive correlation was detected between tPD-L1 and sPD-1 levels (R2=0.426, P<0.001). The median sPD-1 level increased linearly with tPD-L1 score (P=0.002). During the follow-up period, HCC recurred in eight (11.1%) patients and liverrelated mortality occurred in eight (11.1%) patients. Higher sPD-L1 levels (≥19.18 pg/mL) tended to be associated with liver-related mortality (hazard ratio 6.866; 95% confidence interval, 0.804-58.659, P=0.078). sPD-1 levels of patients treated with nivolumab as a second-line therapy changed serially, and a >50% reduction in sPD-1 levels was observed immediately after nivolumab administration. However, sPD-1 level was not associated directly with prognosis in patients with advanced HCC.
Conclusions
The results demonstrated that PD-L1 and PD-1 levels changed according to the immunotherapy. However, no significant association with clinical outcome in patients with HCC was detected. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go
Pil Soo Sung, Isaac Kise Lee, Pu Reun Roh, Min Woo Kang, Jaegyoon Ahn, Seung Kew Yoon
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1): A possible biomarker in predicting post-treatment outcomes in patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma
Tudor Mocan, Maria Ilies, Iuliana Nenu, Rares Craciun, Adelina Horhat, Ruxandra Susa, Iulia Minciuna, Ioana Rusu, Lavinia-Patricia Mocan, Andrada Seicean, Cristina Adela Iuga, Nadim Al Hajjar, Mihaela Sparchez, Daniel-Corneliu Leucuta, Zeno Sparchez
International Immunopharmacology.2021; 94: 107467. CrossRef - Interfacial interactions of SERS-active noble metal nanostructures with functional ligands for diagnostic analysis of protein cancer markers
Han-Jung Ryu, Won Kyu Lee, Yoon Hyuck Kim, Jae-Seung Lee
Microchimica Acta.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Status and Future Direction of Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Do the Data Suggest?
Hye Won Lee, Kyung Joo Cho, Jun Yong Park
Immune Network.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Nivolumab for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Multiple Lung Metastases after Sorafenib Failure
Jaewoong Kim, Jin Won Chang, Jun Yong Park
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(1): 72. CrossRef
- Blood-based biomarkers for immune-based therapy in advanced HCC: Promising but a long way to go

- Subclassification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Intermediate Stage
- Hye Won Lee, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Snag Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Beom Kyung Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2016;16(1):17-22. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.16.1.17
- 1,311 Views
- 13 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background/Aim
s: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) intermediate stage includes a highly heterogeneous population. Here, we aimed to subclassify hepatocellular carcinoma with BCLC intermediate stage for better prognostification.
Methods
Between 2003 and 2008, 325 patients who were newly diagnosed as HCC with BCLC intermediate stage were considered eligible. Tumor factor and liver function were used for sub-classification. Overall survival (OS) was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method with a comparison by log-rank test.
Results
A total of 325 patients with intermediate stage HCC were analyzed. Patients with tumor size ≥7 cm, tumor number ≥4 and Child-Pugh class B had the worse OS compared to those with tumor size <7 cm, tumor number <4 and Child-pugh class A, respectively (all P<0.05). These three variables affected the OS independently from multivariate Cox regression analysis (all P<0.05). So, using these three variables, patients were finally sub-classified as those with fulfilling none of three factors (B-a), one of three factors (B-b), two of three factors (B-c) and all of three factors (B-d) with the median OS of 39.2, 20.6, 12.0 and 8.3 months with statistical significances (all P<0.05 between B-a and B-b, between B-b and B-c, and between B-c and B-d), respectively.
Conclusions
Sub-classification of HCC with BCLC intermediate stage may be useful in not only prognostification but also guidance of treatment strategies. (J Liver Cancer 2016;16:17-22)

Case Reports
- A Case of Rapidly Recurred Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Distant Metastasis after Surgical Resection
- Mi Yeon Kim, Hye Won Lee, Kyu Sik Jung, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Do Young Kim
- J Liver Cancer. 2015;15(2):136-139. Published online September 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.15.2.139
- 890 Views
- 7 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the cancers with poor prognosis. However, surgical resection is the treatment of choice as curative aim for early HCC with preserved liver function. A 5 year survival rate after curative resection is over 50%. We experienced a case of rapidly recurred HCC with bone metastasis after surgical resection. In our case, microscopically microvessel invasion was present after resection. Microvascular invasion (MVI) is an important factor to influence survival and/or HCC recurrence. So we suggested the patients with MVI need to follow up intensively and adjuvant therapy may be considered.

- A Case of Partial Response of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Induced by Concurrent Chemoradiation and Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy after Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization
- Myung Eun Song, Sangheun Lee, Mi Na Kim, Dong-Jun Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Chae Yoon Chon, Kwang-Hyub Han, Jinsil Seong, Do Young Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(2):152-157. Published online September 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.2.152
- 946 Views
- 7 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 63-year-old man patient was referred for treatment of infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma with hilar invasion after transarterial chemoembolization. Serum alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin were elevated, liver dynamic CT showed infiltrative type mass in left hepatic lobe and right hepatic dome with hilar invasion and left intrahepatic duct dilatation. Also CT showed obliteration of left portal vein and metastasis of lymph node around common bile duct. He was diagnosed as hepatocellular carcinoma (UICC stage IV-A, BCLC stage C). With the percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage and the concurrent chemoradiation therapy and the 4th cycle of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy for infiltrative mass, viable tumor was decreased in resectable size at eight months from initial diagnosis.

- A Case of Recurred Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Treated by Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization
- Sangheun Lee, Mi Na Kim, Young Eun Chon, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Chae Yoon Chon, Kwang-Hyub Han
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2013;13(1):74-79. Published online February 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.13.1.74
- 1,053 Views
- 4 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocelluar carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer in the world and the most prevalent cancer among patients liver cirrhosis. The management of HCC depends on tumor stage and the degree of liver dysfunction. Patients with intermediate-stage HCC are ineligible for surgical or local ablative treatments. Current treatment guidelines recommend trans-arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for intermediate stage of HCC. However, tumor recurrence after TACE is universal and the survival benefit is relatively small. Hence, new strategies are needed to improve the outcome of HCC patients undergoing TACE. Recently, the combination of target agents with TACE has shown promising overall survival in advanced HCC. It is necessary to investigate new treat strategy how to increase treatment outcome of advanced HCC by new treat strategy.

- A Case of Necrotizing Pancreatitis after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Mi Na Kim, Jung Hyun Cho, Young Eun Chon, Beom Kyung Kim, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(2):155-159. Published online September 30, 2012
- 555 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Acute pancreatitis is a rare but severe postprocedural complication after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) of hepatocellular carcinoma with an incidence of 1.7-4%. The proposed mechanism of this complication is inadvertent embolization through collateral vessels or regurgitation of chemotherapeutic agents to the arteries of other organs. Here, we present a fatal necrotizing pancreatitis case which developed 10 days after TACE, caused by the regurgitation of the chemotherapeutic agents to the pancreas during the procedure. The patient recovered with conservative care at first, but after suffering from several times of recurrent pancreatitis, he died of peritoneal septic shock 5 months after the initial pancreatitis attack.

- A Case of Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma which was Supervening with Renal Cell Cancer Cured by Repeated Transarterial Chemoembolization and Sorafenib after Resection
- Bun Kim, Jae Hoon Min, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Kwang Hoon Lee, Do Youn Lee, Jin Sub Choi, Young Deuk Choi, Nam Hoon Cho, Young Nyun Park, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon, Do Young Kim
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2012;12(1):51-57. Published online February 28, 2012
- 470 Views
- 2 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is difficult to treat and the survival is poor. Here, we present a patient diagnosed as advanced HCC (stage IIIa) which was supervening with early renal cell cancer (stage I). The patient was treated with pre-operational transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and surgical resection (right hepatectomy, right nephrectomy, and cholecystectomy). Sorafenib were taken continually after surgery. Multiple recurred HCC nodules in remnant liver were detected 2 months later after surgery. Combined treatment modalities including 4 sessions of TACE, and 12 cycles of 5-flurouracil (FU)/carboplatin based hepatic arterial infusional chemotherapy (HAIC) induced complete response. After the diagnosis of advanced HCC, the patient survived 36 months and experienced disease-free status for 19 months.

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurred Extensively during Treatment of Biliary Complication Occurring after Transarterial Chemoembolization
- Hyun Jung Oh, Hana Park, Kwang Hoon Lee, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon, Jun Yong Park
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2011;11(2):178-184. Published online September 30, 2011
- 518 Views
- 3 Downloads
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) is one of the cancers with poor prognosis. Transarterial chemoembolization(TACE) has been widely used for treating unresectable HCC. Although TACE is considered as a less invasive and relative safe procedure, severe complications such as hepatic failure, pulmonary embolism, liver abscess, biloma formationcan occur rarely after TACE. These complications sometimes may lead to fatal clinical situation, even death. We reported a case of HCC recurred extensively during treatment of biliary complication after TACE. A 44-year-old male with HCC was admitted due to fever for 3 days after undergoing TACE. Three weeks before the admission, he had been diagnosed with HCC recurrence which presented as two arterial enhancing nodules in MRI and treated with TACE. CT scan showed 7 cm sized air containing fluid collections with necrosis suggestive of liver abscess and 15 cm sized biloma formation. Because the patient was in septic shock at admission, percutaneous catheter drainage was performed with use of broad spectrum antibiotics. After treatment of 3 months, the sizes of hepatic abscess and biloma were remarkably decreased. However, 1 month later, large size tumor recurrence and perihepatic lymph node metastasis were found on a follow-up CT scan. In this case, the cause of rapid growing recurrence after TACE is uncertain, but the development of unanticipated complication seems to affect the progression to poor prognosis. Therefore, early recognization of predisposing factors with proper management would be needed to prevent these serious complications after TACE.

- A Case of Hepatocellular Carcinoma showing Progressive Disease in Systemic Chemotherapy, but Partial Response in Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy with the Same Regimen
- Soung Min Jeon, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang Hyub Han, Chae Yoon Chon, Jun Yong Park
- Journal of the Korean Liver Cancer Study Group. 2010;10(1):44-48. Published online June 30, 2010
- 517 Views
- 0 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third most common malignancy in Korea. Despite recent advances in the area of HCC, a considerable number of HCC patients require non-surgical treatments and systemic therapies because of poor liver function or intermediate to advanced cancer stages at the time of diagnosis. Unfortunately, chemotherapy for advanced HCC has limited response rates and provides a marginal survival benefit. Several studies have supported potential advantages of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC), designed to improve chemotherapy benefits by increasing the amount of chemotherapy delivered to the site of the tumor and to minimizes the side-effects of the chemotherapy. However, there hasn’t been any report showing different responses between systemic chemotherapy and HAIC for the same patient. Herein, we report a case of HCC showing progressive disease in systemic chemotherapy, but partial response in HAIC with the same regimen for the same patient with portal vein thrombosis. This case implies HAIC might be alternative option for HCC patient showing ineffective response to systemic chemotherapy, even with the same regimen.


 E-submission
E-submission THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION
THE KOREAN LIVER CANCER ASSOCIATION

 First
First Prev
Prev



 Follow JLC on Twitter
Follow JLC on Twitter